In the maze of human experience, there’s a lot to understand about why some people turn to substance abuse. It’s not just one thing—a mix of factors that come together. Some of it is in our genes, passed down from our parents like an invisible hand guiding our choices. But it’s not just biology that plays a role; our surroundings have a big say too. Where we live, who we’re around, and even how we feel inside all play a part. Understanding and addressing these risk factors is crucial to developing effective prevention and intervention strategies to mitigate the impact of substance abuse on individuals and communities.
What Makes Some People More Vulnerable To Addiction?
Jump to Section
Some individuals are more prone to drug addiction due to specific circumstances or conditions. However, these factors alone do not determine one’s destiny. Instead, addiction vulnerability arises from a complex interplay of biological, environmental, and psychological elements, which can be influenced and alleviated through education, prevention strategies, and appropriate support systems.
Genetics
Genetics plays a significant role in determining a person’s susceptibility to addiction, as certain genes can increase the likelihood of developing addictive behaviors. Additionally, individuals with a family history of addiction are more likely to struggle with substance abuse themselves.
Psychological and Environmental Factors
Psychological and environmental factors can also contribute to vulnerability to addiction. Individuals who have experienced trauma, abuse, or neglect may turn to substances as a coping mechanism, leading to addiction. Moreover, individuals who are surrounded by peers who engage in substance abuse may be more likely to develop addictive behaviors.
Mental Health Disorders
Mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, ADHD, and PTSD can also increase vulnerability to addiction, as individuals may use substances to self-medicate unpleasant symptoms. Additionally, chronic stress, poor coping skills, and a lack of social support can all contribute to an increased risk of addiction.
Age of First Use
The age of first use is crucial; early alcohol, nicotine, or substance intake indicates a higher susceptibility to addiction.
Which Substances Are More Addictive Than Other Drugs?

Substances vary in addictive potential based on their impact on the brain’s reward system and the severity of withdrawal symptoms. Here are a few substances that are commonly regarded as more addictive than others:
Nicotine
Nicotine, a potent alkaloid found in tobacco, swiftly binds to brain receptors, releasing dopamine and fostering dependence over time. Its addictive properties stem from its ability to trigger pleasure sensations and fuel a compelling urge for continued use.
Heroin
Heroin is an opioid drug that stands as one of the most addictive substances known to humanity. Heroin’s appeal lies in its quick euphoria and profound well-being by flooding the brain with dopamine and endorphins. This draws repeated use for fleeting bliss. We can assist you with our heroin rehab center.
Cocaine
Cocaine, a potent stimulant from the coca plant, profoundly affects brain chemistry, inducing euphoria and heightened alertness. It hijacks dopamine pathways, causing surges. This flood of dopamine induces sensations of unparalleled pleasure and confidence, rendering the user momentarily invincible. We can assist you with our cocaine rehab center.
Methamphetamine
Methamphetamine, commonly known as meth, swiftly elevates dopamine levels in the brain, inducing a surge of euphoria and heightened alertness. This rapid increase in dopamine, the neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward, fosters intense feelings of well-being and invigoration. We can assist you with our meth rehab center.
Alcohol
Alcohol, a ubiquitous and socially accepted substance, holds a complex duality in modern society. While it is commonly enjoyed in moderation, its addictive potential and detrimental health effects cannot be overlooked. Derived from fermented grains, fruits, or other sources, alcohol exerts its influence on the body and mind with profound consequences. Chronic alcohol use can lead to physical dependence and severe withdrawal symptoms, including tremors, hallucinations, and seizures. We can assist you with our alcohol rehab center.
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines are a class of prescription medications commonly prescribed to alleviate symptoms of anxiety, insomnia, and other related disorders. This drug serves as a double-edged sword in the realm of pharmacotherapy. While it offers relief for many individuals grappling with these debilitating conditions, its potent effects on the central nervous system go hand in hand with a significant risk of addiction and dependency. We can assist with our benzo rehab center.
While various substances differ in their addictive properties, all have the potential to disrupt brain chemistry and induce dependence. Understanding the mechanisms underlying addiction is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies to combat substance abuse and its devastating consequences for individuals and society.
Why Substance Use In Young Adults Is A Major Concern?
According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), young adults aged 18 to 26 are more vulnerable to drug use and substance abuse in the United States. Numerous factors contribute to the high levels of drug and alcohol use among this demographic, including:
Brain Development
Young adulthood is a crucial period for brain development, particularly the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for decision-making, impulse control, and judgment. Substance use during this time can disrupt normal brain development, leading to long-term cognitive impairments and behavioral problems.
Health Risks
Substance use can have detrimental effects on physical health, including an increased risk of heart disease, liver damage, respiratory issues, and various cancers. It can also weaken the immune system, making young adults more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
Mental Health
Substance use is closely linked to mental health issues such as depression, anxiety, and psychosis. Many young adults turn to substances as a way to cope with stress, trauma, or underlying mental health disorders, but in reality, substance use often exacerbates these problems and can lead to addiction.
Academic and Occupational Impact
Substance use can interfere with academic performance and hinder educational attainment. It can also jeopardize future career prospects by impairing job performance, reducing productivity, and increasing the risk of unemployment or underemployment.
Social Consequences
Substance use can strain relationships with family and friends, leading to conflicts and social isolation. It may also contribute to risky behaviors such as unprotected sex, driving under the influence, and criminal activities, which can have serious legal and social repercussions.
Risk of Addiction
Young adulthood is a critical period of vulnerability for the development of substance use disorders. Early initiation of substance use increases the risk of addiction later in life, making it difficult for young adults to break free from harmful patterns of behavior and leading to a lifelong struggle with addiction.
Financial Burden
Substance use imposes a significant financial burden on individuals, families, and society as a whole. The costs associated with healthcare expenses, legal fees, lost productivity, and social welfare programs place a strain on resources that could be allocated to more constructive endeavors.
Substance use in young adults poses a multitude of challenges and risks that can have far-reaching consequences for their health, well-being, and prospects. Addressing this issue requires a comprehensive approach involving education, prevention, early intervention, and access to effective treatment and support services. We offer a young adult treatment program.
How Can Substance Abuse Disorders in Young Adults Be Effectively Treated?
Treating substance abuse in young adults requires a comprehensive approach targeting both physical and psychological aspects of addiction. Here are several effective strategies:
Detoxification
In cases of physical dependence, detoxification under medical supervision may be necessary to safely manage withdrawal symptoms.
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT)
MAT involves the use of medications, such as methadone, buprenorphine, or naltrexone, alongside counseling and behavioral therapies to help manage cravings and prevent relapse, particularly in opioid addiction and alcohol addiction.
Psychotherapy
Various forms of psychotherapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), motivational interviewing, and contingency management, can help young adults understand the root causes of their substance abuse, develop coping strategies, and build healthier behaviors.
Family Therapy
Including family in treatment offers vital support and addresses dynamics contributing to substance abuse among young adults.
Support Groups
Participation in support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or Narcotics Anonymous (NA) can offer peer support, accountability, and a sense of belonging to young adults in recovery.
Holistic Therapies
Incorporating holistic therapies such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, art therapy, and recreational activities can help young adults develop new interests and coping mechanisms while reducing stress.
Aftercare Planning
Developing a comprehensive aftercare plan that includes ongoing therapy, support group participation, regular medical check-ups, and vocational or educational assistance can help young adults transition successfully back into their communities and reduce the risk of relapse.
It’s important to recognize that treatment approaches should be tailored to individual needs and may require adjustments over time. Additionally, ongoing support and monitoring are crucial for sustaining long-term recovery in young adults with substance abuse disorders.
Free by the Sea Can Help You Understand Risk Factors For Substance Abuse
At Free by the Sea, we’re committed to empowering individuals with the knowledge they need to navigate the complexities of substance abuse. By understanding the risk factors associated with addiction, you can take proactive steps toward prevention and seek the support necessary for recovery. Our comprehensive resources and compassionate approach ensure that you’re not alone in this journey. Together, let’s break free from the chains of substance abuse and embrace a healthier, happier life. Take the first step towards empowerment today. Contact us!
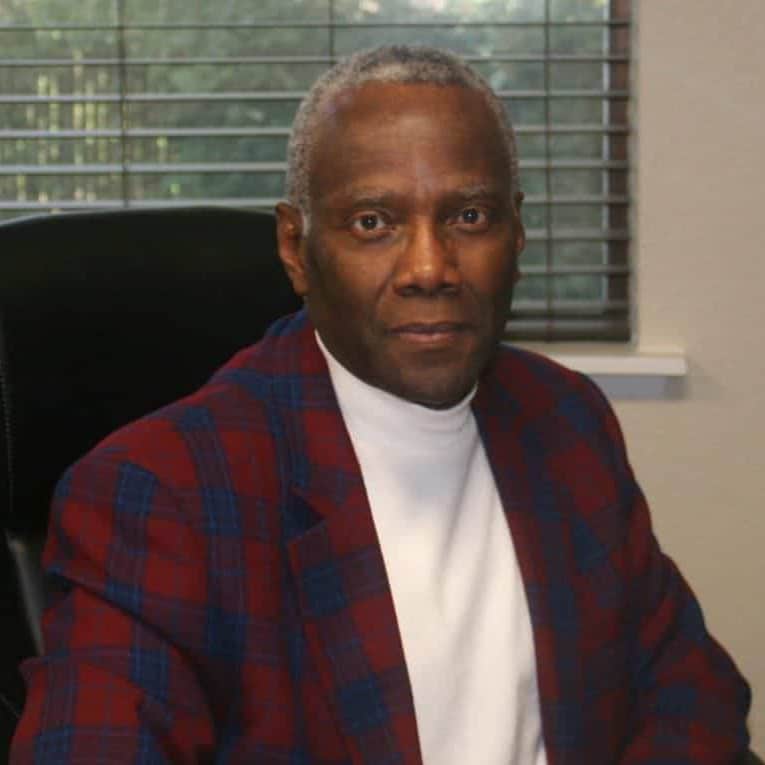

Dr. Richard Crabbe joined our team in 2019 as our psychiatrist and medical director. He attended the University of Ghana Medical School where he became a Medical Doctor in 1977. From 1978 through 1984, he was a medical officer in the Ghana Navy and provided a variety of services from general medicine to surgeries. He received his Certificate in General Psychology from the American Board of Psychology and Neurology in 2002.

 April 8th, 2024
April 8th, 2024










