When we get questions about how long alcohol stays in the system, we explain that the answer depends on the type of test being used. Alcohol itself typically remains detectable in your blood for 8 to 12 hours after drinking, but metabolites like ethyl glucuronide (EtG) can show up in urine tests for up to 5 days. These detection windows matter to you whether you’re dealing with workplace testing, meeting legal requirements, or worried about your own drinking habits.
How quickly alcohol leaves your system depends on your unique circumstances. Your body’s metabolism, weight, age, and how much you drank all affect elimination time. While breath tests detect alcohol for up to 24 hours, urine metabolite tests extend that window significantly—making them common tools for monitoring sobriety in treatment programs and legal settings.
At Free by the Sea in Washington, we know that when people ask about alcohol detection times, they’re often worried about their drinking and how it’s affecting their lives. Our team provides compassionate, evidence-based care for individuals and families navigating alcohol-related challenges. Whether you’re seeking information for yourself or a loved one, professional support can help you understand your options and take meaningful steps toward recovery.
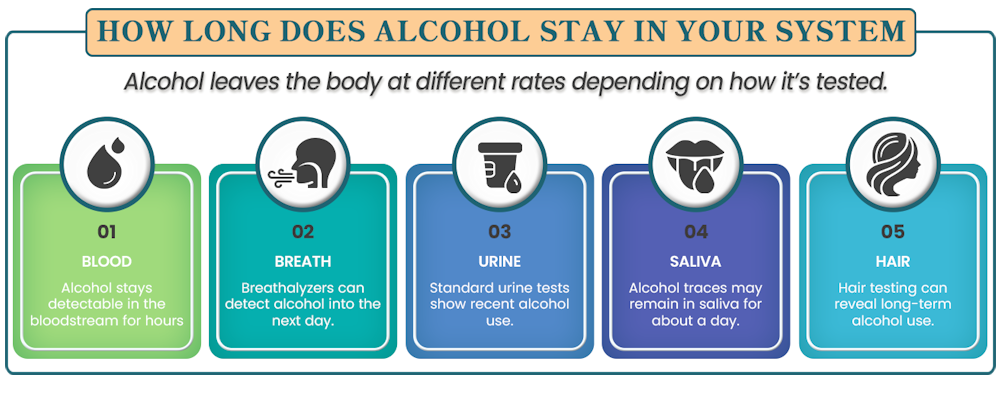
How Long Does Alcohol Stay in Your System by Test Type
How long tests can detect alcohol in your system varies widely depending on the testing method. The table below compares all major testing methods, showing both direct alcohol detection and metabolite detection timeframes.
Blood Alcohol Detection Timeline
Blood tests measure ethanol directly, offering the most accurate snapshot of current alcohol levels. The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism reports that alcohol typically stays detectable in your blood for 8 to 12 hours after drinking. Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) typically peaks within 1.5 to 2 hours after drinking.
Here’s what happens as your body processes alcohol:
- 0 to 2 hours: BAC rises as alcohol absorbs into your bloodstream and reaches peak levels
- 3 to 8 hours: Direct ethanol remains detectable as your liver processes the alcohol
- Up to 36 hours: EtG metabolites can still be identified in blood samples
Urine Alcohol Detection Timeline
Urine testing is one of the most common methods for detecting alcohol use in workplace programs and treatment settings. Standard urine tests identify ethanol for 7 to 12 hours after drinking. However, metabolite testing extends this window considerably—EtG and EtS can be detected for 2 to 5 days.
Treatment programs rely on urine tests specifically because they can detect alcohol use for days, not just hours. A single moderate drinking episode may produce detectable EtG levels for 24 to 48 hours, while heavy drinking can result in positive tests for up to 5 days.
Breath Alcohol Detection Timeline
Breathalyzers detect alcohol for up to 24 hours after consumption. These devices measure breath alcohol levels that correlate directly with blood alcohol concentration. Law enforcement and employers prefer breath tests because they provide immediate results and reflect current impairment levels.
Your metabolism speed, body weight, and recent consumption patterns all affect breath test accuracy. A single drink may clear from your breath in 1 to 2 hours, while heavy drinking episodes can extend detection times to the full 24-hour window.
Saliva and Hair Follicle Detection
Saliva tests detect alcohol for 12 to 48 hours and offer a convenient, non-invasive testing option. Hair follicle tests serve a different purpose—they identify patterns of heavy drinking for up to 90 days. These tests are used to assess chronic alcohol use rather than occasional drinking.
Signs That Alcohol Use May Be Becoming a Problem

Knowing how long alcohol stays in your system matters most when you’re worried about your drinking habits.
Physical Warning Signs
Your body provides clear signals when alcohol use becomes problematic. Tolerance develops when your body adapts to regular alcohol consumption, requiring more drinks to feel the same effects. Withdrawal symptoms appear when alcohol leaves your system after regular heavy use—common symptoms include tremors, sweating, nausea, anxiety, and sleep disturbances.
Health complications from drinking include:
- Liver damage: Chronic use can lead to fatty liver, hepatitis, or cirrhosis
- Cardiovascular problems: High blood pressure and increased heart disease risk
- Digestive issues: Stomach inflammation and increased cancer risk
Behavioral and Emotional Changes
Drinking patterns often shift when alcohol use becomes concerning. People may drink earlier in the day, hide their consumption, or drink alone more frequently. Using alcohol to manage stress, anxiety, sadness, or other emotions signals a problematic relationship with drinking.
Attempts to reduce or stop drinking that repeatedly fail indicate loss of control. You may set limits on how much you’ll drink, but consistently exceed them. Mood changes related to drinking include irritability when unable to drink, depression, or anxiety.
Impact on Work and Relationships
Alcohol-related absences from work or school create noticeable patterns. Hangovers, illness from drinking, or prioritizing alcohol over responsibilities lead to missed days. Relationships suffer when alcohol becomes a priority—family members and friends may express concern about drinking habits.
Relationships suffer when alcohol becomes a priority, and family members or friends may express concern about drinking habits. If these signs are familiar, we find that alcohol addiction treatment can provide the support needed for recovery.
What Factors Affect How Long Alcohol Stays in Your System
Several personal and situational factors determine how long alcohol remains detectable in your body. These differences explain why two people can drink identical amounts but have different elimination timeframes.
Age and Gender Differences
Metabolism slows with age, so older adults process alcohol more slowly than younger individuals. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, people over 65 may experience blood alcohol concentrations up to 20% higher than younger adults after consuming the same amount.
Women typically have higher BACs than men after drinking equal amounts. This occurs because women generally have less water in their bodies and lower levels of ADH—the enzyme that begins breaking down alcohol in the stomach before it enters the bloodstream.
Body Weight and Composition
Higher body mass and lower body fat percentage can dilute alcohol, leading to lower BAC. A person weighing 180 pounds will typically process the same amount of alcohol faster than someone weighing 120 pounds.
Body fat contains less water than muscle tissue, so alcohol becomes more concentrated in people with higher body fat percentages. This concentration affects both intoxication levels and detection times.
Liver Health and Metabolism
Your liver breaks down alcohol at approximately one standard drink per hour. Liver damage or disease significantly slows this process, extending detection times. Enzymes like ADH and ALDH help process alcohol, and genetic differences affect their efficiency.
Studies indicate that approximately 40% of East Asian populations have a variant ALDH enzyme that slows alcohol metabolism. Some people inherit enzyme variants that produce less efficient versions, causing alcohol and its metabolites to remain in the system longer.
Amount and Type of Alcohol Consumed
The more alcohol you drink, the longer the elimination takes. Each additional drink adds approximately one hour to the elimination time, though this varies based on individual factors. A standard drink contains roughly 0.6 ounces of pure alcohol—equivalent to one 12-ounce beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1.5 ounces of distilled spirits.
The type of alcohol (beer, wine, liquor) doesn’t significantly change metabolism rate. What matters is the total amount of ethanol consumed, not the beverage type.
Food Consumption and Hydration
Eating food slows alcohol absorption by keeping it in your stomach longer before entering your bloodstream. Meals high in protein and fat are particularly effective at slowing absorption rates. Hydration helps your body eliminate alcohol more efficiently through urine and other bodily processes.
Practical tips include:
- Eat before or while drinking: Food in your stomach reduces peak BAC by 20-30%
- Stay hydrated: Alternating alcoholic drinks with water helps maintain hydration and may reduce overall consumption
Frequently Asked Questions about Alcohol Detection and Recovery
Can you speed up how quickly alcohol leaves your system?
No, you cannot significantly speed up alcohol elimination. Your liver processes alcohol at a fixed rate of approximately one standard drink per hour, regardless of what you do. Common myths like drinking coffee, taking cold showers, or exercising do not accelerate the breakdown of alcohol already in your bloodstream.
How accurate are at-home alcohol tests?
Professional laboratory tests are more accurate than at-home devices because they use standardized methods to detect ethanol and its metabolites with high precision. Home testing kits and personal breathalyzers vary in sensitivity and may not be properly calibrated.
What happens during professional alcohol detox?
During professional detox, medical staff provide 24/7 monitoring and use medications to safely manage withdrawal symptoms like tremors, anxiety, and seizures. This supervision reduces the risk of dangerous complications during the 3-to-7-day process.
How can family members help someone with alcohol concerns?
Family members can help by expressing concern without judgment and offering to research treatment options. Learning about alcohol use disorder helps them set healthy boundaries while providing support.
Does insurance cover alcohol addiction treatment?
Yes, most insurance plans cover addiction treatment due to federal laws requiring parity with medical condition coverage. Specific benefits and costs will vary depending on your plan, deductible, and provider network.
If you or someone you care about is struggling with alcohol concerns in Washington, don’t hesitate to reach out for help. Contact Free by the Sea to learn more about your options and verify your insurance coverage. Recovery is possible, and support is just a call or click away.

Dr. Richard Crabbe joined our team in 2019 as our psychiatrist and medical director. He attended the University of Ghana Medical School where he became a Medical Doctor in 1977. From 1978 through 1984, he was a medical officer in the Ghana Navy and provided a variety of services from general medicine to surgeries. He received his Certificate in General Psychology from the American Board of Psychology and Neurology in 2002.
Insurances We Accept
Free by the Sea recognizes the importance of having insurance to receive addiction treatment. Let us work with you to provide you or a loved one with premier addiction treatment services. We accept several private insurance plans. Verify your rehab coverage with us today to ensure you receive the support that you need! Find out if you are covered today!











